Glossary
Cluster
Equivalent to the concept of a cluster in Kubernetes, such as a cluster named democluster.
Karpor can manage multiple clusters, including cluster registration, certificate rotation, generating and viewing insights, and other operations through a Dashboard. It also supports accessing any managed cluster using a unified certificate issued by Karpor through command-line tools such as kubectl and kubectx.
For more details, please refer to the best practice: One Pass with Proxy.
Resource
Equivalent to the resource concept in Kubernetes, such as a Deployment named mockDeployment.
Karpor performs real-time synchronization, search, and insights on resources within the managed clusters. A resource is the object with the smallest granularity for searching and insights in Karpor.
Resource Group
A resource group is a logical organizational structure used to combine related Kubernetes resources for a more intuitive view, search, and insight experience. For example, an Application named mockapp resource group can be created to includes a Namespace, a Deployment, and multiple Pods, all with a specific label such as app.kubernetes.io/name: mockapp.
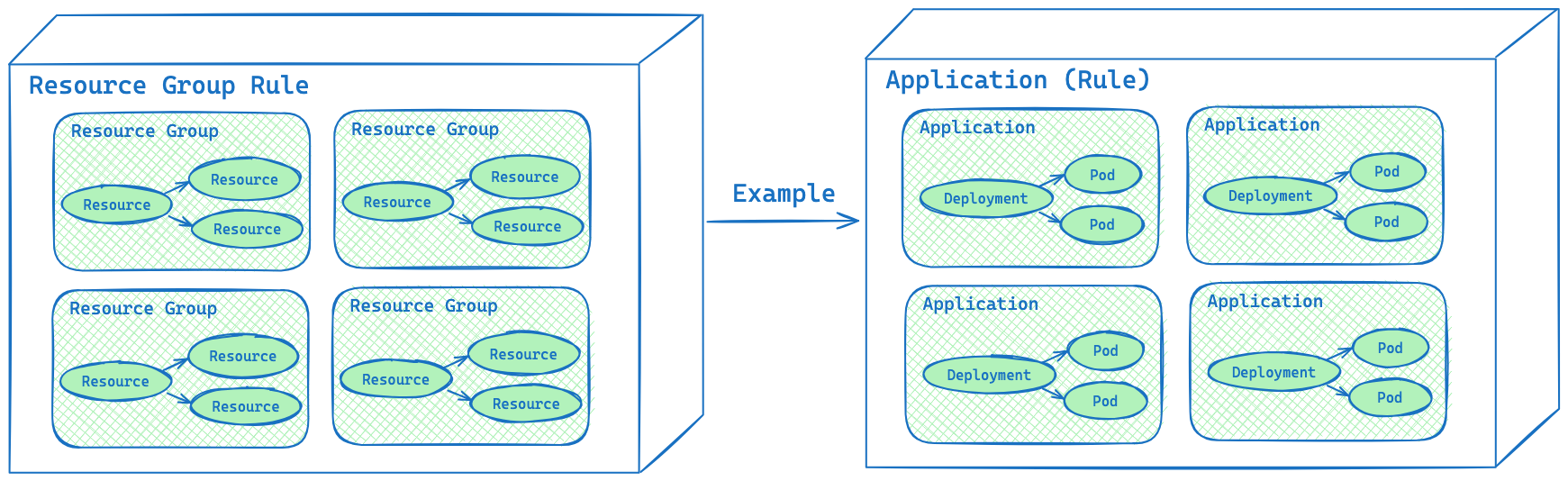
Resource Group Rule
A resource group rule is a set of conditions that groups specific resources into appropriate resource groups. These rules aim to organize resources into logical units based on properties such as annotations, labels, namespace, and so on. For example, to define an Application resource group rule, you can specify the app.kubernetes.io/name annotation as a grouping condition.
Karpor has a preset resource group rule - Namespace - as well as custom resource group rules.
Topology
In Karpor, the topology refers to the relations and dependencies between relevant resources within a given resource group. Viewing and understanding the interior structure of a resource group is made easier with a visual topology diagram, which is helpful for troubleshooting and locating issues.
Audit
Audit refers to performing a compliance scan on all resources within a given resource group. The goal is to help users discover potential risks. The scanning tools and rules used for the audit are currently built into the system, but we will support customization in the future.
Issue
The output of the audit is referred to as issues. If there are no problems with the scanned object, the audit results will be empty. Otherwise, all identified risks will be categorized by their risk level and displayed, including descriptions of each risk, associated resources, etc., guiding users to fix the issues, ensure the security and compliance of the cluster resources.
Score
The score is used to reflect the overall health status of a resource group or a resource, reminding users to take timely adjustments and measures. The health score is calculated based on the resource group's audit results. The factors that impact the score include: risk level, number of risks, and total number of resources.
Next Step
- Learn Karpor's Architecture.
- View User Guide to look on more of what you can achieve with Karpor.