Deploy Application Securely and Efficiently via GitHub Actions
This document provides the instruction to deploy your application securely and efficiently via GitHub Actions.
Using git repository is a very reliable and common way to manage code, and the same goes for Kusion-managed configuration code. GitHub Actions is a CI/CD platform. By customizing GitHub Actions workflow, the pipeline such as building, testing, and deploying will be executed automatically.
Kusion has a commendable integration with GitHub Actions. You can use GitHub Actions to test configuration correctness, preview change, and deploy application. This tutorial demonstrates how to deploy and operate an application through GitHub Actions.
GitHub Actions Workflow
KusionStack/konfig is the official example repository, and provides the GitHub Actions workflow deploy. The workflow is triggered by a push on the main branch, and includes multiple jobs, which ensures the reliability of configuration code, and deploys the changed application.
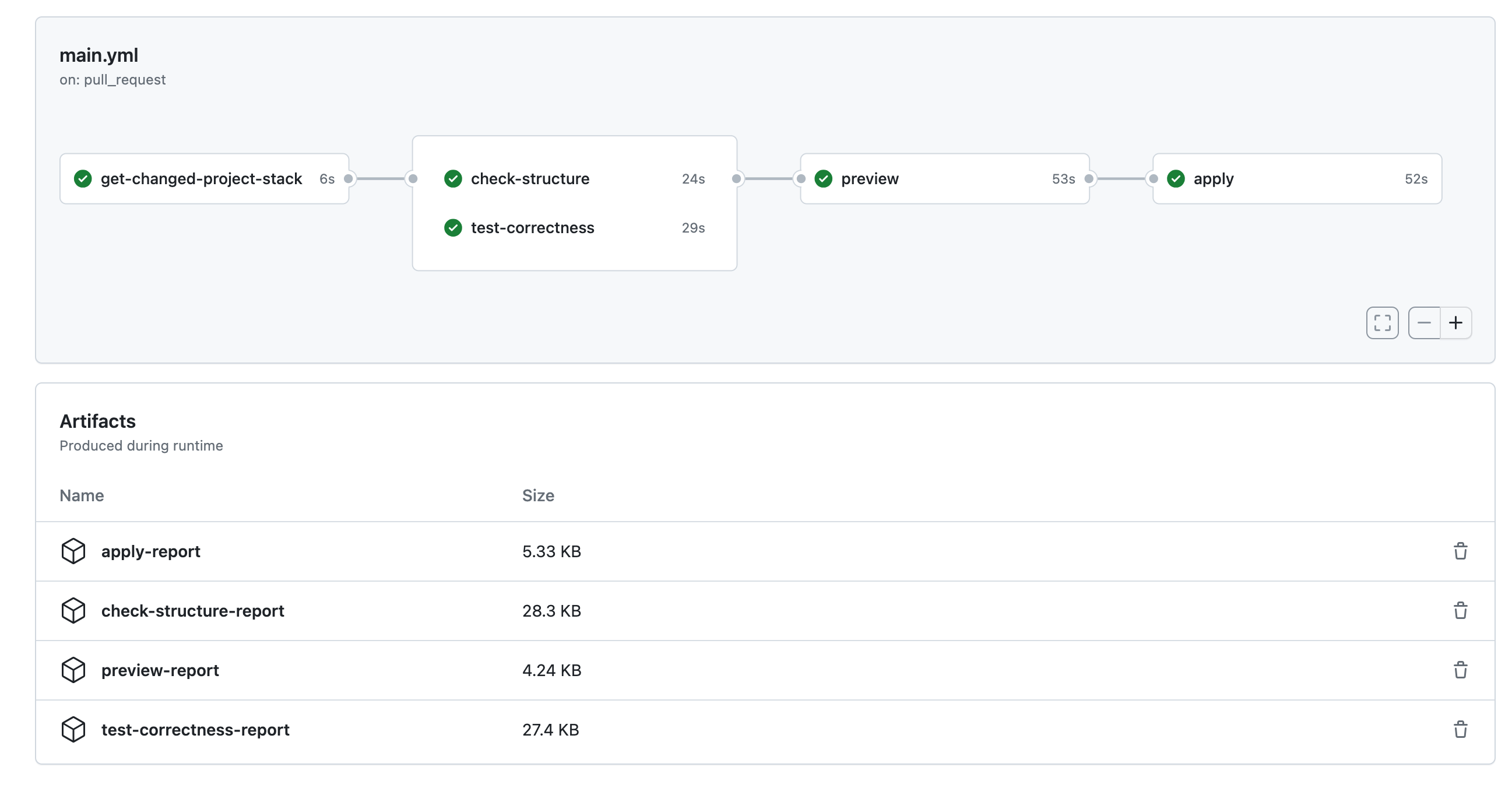
The workflow to deploy an application is shown above, which includes the following jobs:
- Get changed project and stack
- Check project and stack structure
- Test code correctness
- Preview changed stack
- Apply changed stack
These jobs ensure the security and efficiency of the application deployment. Next, this tutorial will introduce the usage and function of these jobs. To show how they work more visually, updating port configuration in file example/service-multi-stack/base/base.k of service-multi-stack (referred to "the example" in the below) is given as an example.
Get Changed Project and Stack
As Kusion organizes code by project and stack, to deploy the affected applications, analyze the changed project and stack is the first step.
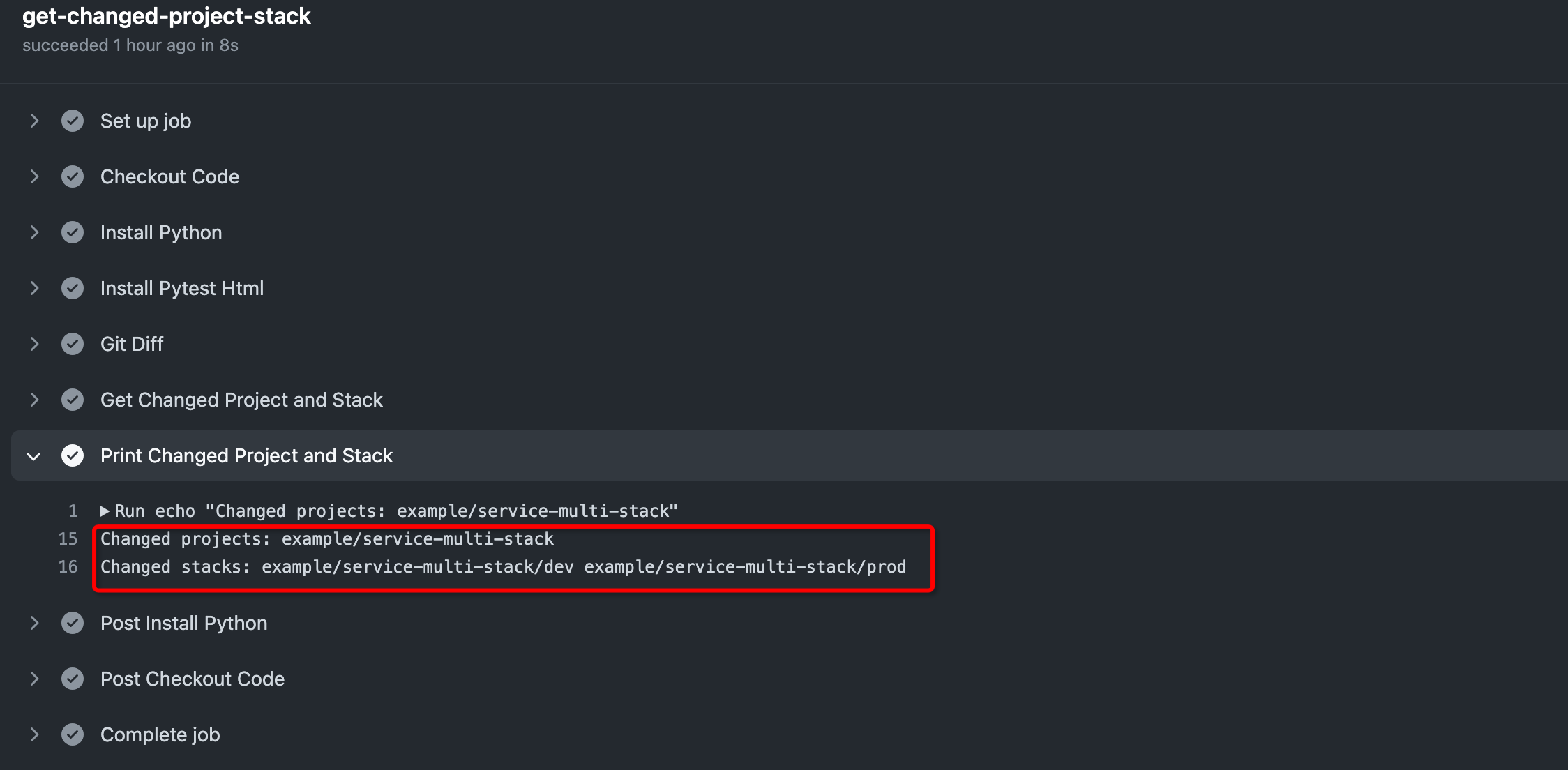
The job, get-changed-project-stack perfectly accomplish the analysis. The main steps are as follows:
- Obtain the list of changed files through
git diff; - Based on the changed file list, obtain the changed projects and stacks which are indicated by
project.yamlandstack.yamlrespectively.
The example changes the file example/service-multi-stack/base/base.k, where the affected project is example/service-multi-stack, and the stack is example/service-multi-stack/dev and example/service-multi-stack/prod. Delightfully, the result, which is shown below, meets our expectation.
Check Project and Stack Structure
The job check-structure guarantees the structure legality of the changed project and stack, so that Kusion CLI tools can be used correctly. The check items are as follows:
- The field
nameis required in project.yaml; - The field
nameis required in stack.yaml.
The success of structure-check means the correctness of structure. A pytest report check-structure-report is also generated, and you can get it from GithHub Actions Artifacts .
The example passes the directory structure verification. It is clear from the report that the changed project and stack have get checked, and the result is passed.
<testsuites>
<testsuite name="pytest" errors="0" failures="0" skipped="0" tests="3" time="0.039"
timestamp="2024-01-11T08:29:52.941858" hostname="cdbc8e525b50">
<testcase classname="hack.check_structure"
name="test_project_structure[example/service-multi-stack]" time="0.001" />
<testcase classname="hack.check_structure"
name="test_stack_structure[example/service-multi-stack/dev]" time="0.001" />
<testcase classname="hack.check_structure"
name="test_stack_structure[example/service-multi-stack/prod]" time="0.001" />
</testsuite>
</testsuites>
Test Code Correctness
Besides a rightful structure, the code must have correct syntax and semantics, and the job test-correctness ensures the correctness. kusion build get executed on the changed stacks. If succeeded, there are no syntax errors; or the configuration code is illegal, and the following application deployment will fail.
In this job, not only the correctness of AppConfiguration is checked, but also the workspace configuration. Hence, you should prepare workspace configuration in advance. Now, the job test-correctness supports you put workspace configuration files under directory workspaces with file name's prefix the same as the workspace name and suffix .yaml. For example, if you have two workspaces named dev and prod, you should provide files workspaces/dev.yaml and workspaces/prod.yaml with corresponding workspace configuration.
The jobs preview and apply also ask for the workspace configuration files.
Putting AppConfiguration and workspace configuration in one repository seems not a good idea. Doing this is to give a simple illustration. You can change it in your real production practice, and you can get more information of AppConfiguration and workspace here.
The report whose name is test-correctness-report get generated.
The example passes the code correctness test. The report shows that the tested stack is example/service-multi-stack/dev and example/service-multi-stack/prod, and the result is passed.
<testsuites>
<testsuite name="pytest" errors="0" failures="0" skipped="0" tests="2" time="1.671"
timestamp="2024-01-11T08:29:53.487470" hostname="dfb68b2d7229">
<testcase classname="hack.test_correctness"
name="test_correctness[example/service-multi-stack/dev]" time="0.856" />
<testcase classname="hack.test_correctness"
name="test_correctness[example/service-multi-stack/prod]" time="0.644" />
</testsuite>
</testsuites>
Preview Changed Stack
After passing the above jobs, security of the configuration change is guaranteed, and it's time to deploy your application. Before applying the change to the real infrastructure, it's necessary to get the expected result of the application deployment. The job preview calls kusion preview to get the expected change result, the result is uploaded to the artifact preview-report. If the result meets your requirement, you can go to the next job and deploy the application.
The example changes stack example/service-multi-stack/dev and example/service-multi-stack/prod. The following picture shows the preview result of example/service-multi-stack/prod, where the result is to create a Kubernetes Namespace, Service and Deployment if call kusion apply.
Generating Intent in the Stack prod...
cloning 'https://github.com/KusionStack/catalog.git' with tag '0.1.2'
Stack: prod ID Action
* ├─ v1:Namespace:service-multi-stack Create
* ├─ v1:Service:service-multi-stack:service-multi-stack-prod-echoserver-public Create
* └─ apps/v1:Deployment:service-multi-stack:service-multi-stack-prod-echoserver Create
Apply Changed Stack
Finally, the last step is arrived, i.e. deploy application. The job apply calls kusion apply to apply the configuration change to the real infrastructure. If the job succeeded, the result will be uploaded to the artifact apply-report.
For the stack example/service-multi-stack/prod in the example, a Kubernetes Namespace, Service and Deployment get created, which is consistent with the preview result.
Generating Intent in the Stack prod...
cloning 'https://github.com/KusionStack/catalog.git' with tag '0.1.2'
Stack: prod ID Action
* ├─ v1:Namespace:service-multi-stack UnChanged
* ├─ v1:Service:service-multi-stack:service-multi-stack-prod-echoserver-public Create
* └─ apps/v1:Deployment:service-multi-stack:service-multi-stack-prod-echoserver Create
Start applying diffs ...
SUCCESS: UnChanged v1:Namespace:service-multi-stack, skip
SUCCESS: Create v1:Service:service-multi-stack:service-multi-stack-prod-echoserver-public success
SUCCESS: Create apps/v1:Deployment:service-multi-stack:service-multi-stack-prod-echoserver success
Apply complete! Resources: 2 created, 0 updated, 0 deleted.
Summary
This tutorial demonstrates how Kusion integrates with GitHub Actions to deploy an application. By structure check, correctness test, preview and apply, Kusion with GitHub Actions enables you deploy application efficiently and securely.